Running an e-commerce business is not just about setting up a digital store and selling products online. Other essential components such as logistics, product configuration, infrastructure, secured payment gateway, and supply chain management are involved as well. We will discuss these components in detail in our upcoming topics.
While there are a number of activities running parallel in the backed, following are the key areas of focus for supply chain management in e-commerce?
- Raw material procurement
- Manufacturing
- Distribution and delivery of the right product to the customer
- Order management
- Order entry
- Managing demand and supply
- Inventory tracking
A well-organized and systematic supply chain is essential for any e-commerce business in order to meet customer expectations and keep operations running smoothly. By streamlining processes and ensuring efficient communication between all parties involved in the supply chain, businesses can keep their customers happy and ensure that orders are fulfilled on time.
Before going further let’s understand first what is supply chain?
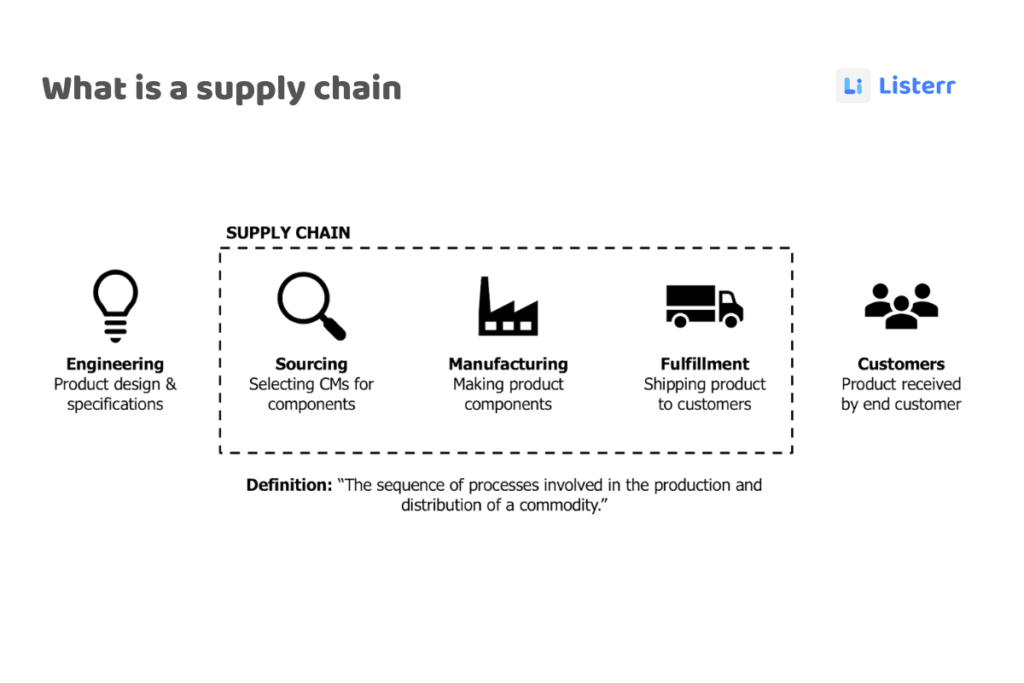
What is a Supply Chain?
Consumer demand for products and services is higher than ever, and everything and everyone involved in getting those services and products to consumers is part of a supply chain. This includes resources, a system of activities, organizations, information, and the people involved.
Consider fresh apples! For these apples to arrive at your breakfast table, a plethora of activities, transactions, and people are in the motion at the backdrop. All these are connected through the internal supply chain and are involved in planting, cultivating, delivering, and consuming apples. The internal supply chain connecting people, establishments, and activities ensures a timely delivery of apples to your doorstep.
Besides the proper flow of physical products like apples, a well-structured works the same way while availing virtual elements such as information and communication.
The term “supply chain” encompasses a lot of moving parts – including people, organizations, and functions – that all play a role in the creation and distribution of products and services. There are four primary activities that make up a supply chain: production, sales, distribution, and fulfillment. Essentially, the supply chain is a value chain. In order to attain maximum value, every member of the chain must coordinate and carry out its function efficiently.
What is digital supply chain?
The digital supply chain is a network of suppliers, manufacturers, logistics providers, and retailers that use digital technologies to manage the flow of goods and information throughout the supply chain. By digitizing the supply chain, businesses can improve visibility, communication, and collaboration among all members of the supply chain. This can lead to improved efficiency and effectiveness in the management of the flow of goods and information.
What is Supply Chain Management (SCM)?
The supply chain is the lifeblood of your business, ensuring the efficient movement of raw materials and finished goods inventory. A proper supply chain management offers an overview from the point of production to getting goods in the hands of the consumer.
More simply put, supply chain management activities are required in order to plan, control, and execute the procurement, manufacturing, and distribution of goods to the end consumer.
Six Digital Supply Chain Trends Transforming the Industry.
1. Data Science: There’s no doubt that data science has revolutionized business and investment over the past decade. But there are still plenty of industries where data science has only just begun to make its mark. Whether it’s developing new products or improving customer service, data science can help businesses in all sorts of ways. And with more and more businesses waking up to the potential of data science, we can only expect even greater advances in the years to come.
Data science is defined as “an interdisciplinary field that uses scientific methods, processes, algorithms and systems to extract knowledge and insights from noisy, structured and unstructured data, and apply knowledge and actionable insights from data across a broad range of application domains.” The key part is the “extraction of knowledge and insights” portion.
Where Data Science Can Help
Logistics: In logistics, data science can help companies to optimize their operations in a number of ways. This includes which delivery routes to take, how to manage fuel more efficiently (including which times of day to travel), and more accurate forecasting of supply and demand. By applying data science in these areas, logistics companies can improve their overall efficiency and performance.
Data science can be applied to logistics in order to help businesses make real-time adjustments as different conditions (such as consumer demand or gas prices) change. DHL’s Smart Truck system uses data science and analytics to calculate the best routes for efficiency, cost and time savings. By using data science to inform their decisions, businesses can optimize their logistics operations for better results.
Supply chain: The supply chain has become a more strategic element of a company’s business. Organizations have started to analyse how to automate demand forecasting, optimize replenishment and lead times, make inventories more accurately reflect market demand, and improve on-time production and delivery.
The goal is to make the supply chain more efficient and predictable. Improved insights can also lead to better agility so that adjustments can be made in real time — and global crises can be successfully weathered. As an example, CIO points out that PepsiCo uses analytics and machine learning to predict out-of-stocks and alert retailers to reorder. By investing in similar technologies, other companies can follow suit and improve their own supply chain management.
Shipping management: Up until recently, there had been little information available about shipping at all, leaving many companies in the dark as to what the rates might be from carriers and how they stacked up against their competitors. Without this analysis, it can be impossible for shippers to understand the impact that shipping costs (and the potential variables that can affect them such as packaging, location, discounts and seasonal rates) have on profitability.
Shipping optimization is a process by which businesses analyse their shipping methods and make adjustments to improve their efficiency and save money. E-commerce Company Nisolo used data analytics to improve its shipping process, resulting in cost savings and improved service. Data science and analytics also enabled Nisolo to plan for future expansion costs.
Manufacturing: There are many ways data science can be applied to manufacturing systems to help make this a reality — monitoring facility processes, modelling maintenance scenarios, recognizing patterns in downtime, reviewing safety practices, and then building out and improving operations to reflect what was learned. Data science can minimize risk, lower costs and improve productivity.
There are many ways data science can be applied to manufacturing systems to help make this a reality — monitoring facility processes, modeling maintenance scenarios, recognizing patterns in downtime, reviewing safety practices, and then building out and improving operations to reflect what was learned. Data science can minimize risk, lower costs and improve productivity.
2. Block chain: A block chain supply chain can help participants record all relevant information about a product, including price, date, location, quality, certification, and more. This information is stored on the block chain, making it more transparent and traceable. As a result, blockchain can help to lower losses from counterfeit and gray market products, improve visibility and compliance over outsourced contract manufacturing, and potentially enhance an organization’s position as a leader in responsible manufacturing.
Blockchain can enable more transparent and accurate end-to-end tracking in the supply chain: Organizations can digitize physical assets and create an immutable record of all transactions, making it possible to track assets from production to delivery or use by end user. This increased supply chain transparency provides businesses and consumers with more visibility into the product journey.
Block chain drives increased supply chain transparency to help reduce fraud for high value goods, such as diamonds and pharmaceutical drugs. By understanding how ingredients and finished goods are passed through each subcontractor, block chain could help companies reduce profit losses from counterfeit and gray market trading. This would also increase confidence in end-market users by reducing or eliminating the impact of counterfeit products.
Furthermore, businesses can maintain more control over outsourced contract manufacturing. Blockchain provides all parties within a respective supply chain with access to the same information, potentially reducing communication or transfer data errors. Less time can be spent validating data and more can be spent on delivering goods and services—either improving quality, reducing cost, or both.

3. Drones Delivery
Drone use in supply chain about to take off!!
The potential for drones to be used as powerful business tools is astounding. For supply chains, drones can be used in warehouses to not only increase accuracy and efficiency of inventory management, but also with last-mile delivery. Drones have the ability to improve various areas of business, and it’s important to explore and take advantage of those possibilities.
The flow of medical supplies during the pandemic is now one of the most recognised-use cases, and many companies are working with the NHS to build drones into the medical supply chain. This has value for time-critical deliveries to remote areas, because certain drugs have a short effective lifespan.
There are also retail delivery examples, where drones provide fast delivery from a network of local retailers.

4. Payment: In a supply chain, the upstream partners, Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs), often get pressured into credit sales, which can add inefficiencies and additional costs that reduce margins throughout the entire supply chain. Meanwhile, large companies that have better financial facilities and lower interest rates still prefer to work with supplier finance. This creates a situation where the large companies always come out ahead while smaller companies lose any potential benefits of being part of the supply chain partnership.
Supply chain finance: By lengthening payment terms to suppliers, businesses can optimize cash flow through supply chain finance – also known as supplier finance or reverse factoring. This set of solutions also provides the option for large and SME suppliers to get paid early.
To know more about Supply chain finance Click Here.
Dynamic discounting: Dynamic discounting is a great way for buyers to save on their Cost of Goods Sold (COGS). This method gives vendors the opportunity to choose when they would like to get paid in exchange for a reduced price. The “dynamic” component refers to the option to vary the discounts based on the dates of payment to suppliers. In most cases, the earlier the payment is made, the greater the discount. This is a great solution for those who want to enhance their profitability!
To know more about Dynamic discounting Click Here.
Payment instrument: There are many different payment options available for supply chain management. Depending on your needs, you can choose from E-rupee, Mudra, Digital Coin, RuPay, UPI, Cards, Cash, or Invoice Discounting. Each option has its own advantages and disadvantages, so be sure to carefully consider your options before making a decision.

5. E-invoicing: The outbreak of COVID-19 has been a major disruption to businesses worldwide, resulting in the need to find new ways of staying connected in an outside-of-office working environment. This has spurred digital transformation at an accelerated pace.
The last several months have also seen a redefinition of operating models, as the old way of working and following procedures has become increasingly ineffective in the New Normal. In some cases, it is simply impossible to execute these procedures as we have done in the past.
One area that was greatly affected by the COVID-19 pandemic was payments. With so many operations moving to online formats, businesses were encouraged to switch to automated payment methods and new digital payment solutions. Electronic invoicing or Cloud-based invoicing, for example, can help streamline the process and support the digitalization and cost-reduction strategies that companies have implemented since the outbreak.
Electronic invoicing or e-Invoicing is simply an exchange of the bills of transactions between the buyer and the supplier, in an electronic format. It eliminates manual handling of invoices for both the supplier and the buyer and facilitates digital record keeping.
E-invoicing will smoothen and optimize the supply chain in effective way. It will enhance the productivity and reduce the operational as well as transportation cost significantly. Industries like FMCG, Fashion, Cosmetics, D2C brands etc. will leverage this facility, and shorten their supply chain in timelines.
6. Digital Warehousing: Warehouses are being developed closer to large commercial hubs to help with the surge in Last-Mile Delivery (LMD). Customers expect speedier delivery, and a strategically located warehouse allows businesses to meet these demands.
Investors in the supply chain are starting to focus on a major improvement from the beginning to the end of the chain so that new technologies can be used in the warehouse. As the e-commerce and LMD industries grow and expand, the accessibility of distribution centers, the technologies they use, and their speed become increasingly important.
Supply chains are important to the proper operation of society, from providing fresh fruits and vegetables to our grocery shops to sending crucial building materials to construction projects. For this reason, making technology-oriented investments in every link of the supply chain opens the window of our future.
The Covid-19 outbreak disrupted supply chains, causing millions of dollars in damages and making it difficult for the public to get numerous products that we take for granted. This showed us how much we need technological innovations in all supply chain rings, especially in warehouses. How can companies strengthen their logistics and put themselves up for success as the world prepares to come back to work?
What does this signify for digital warehousing and management?
In the near future, those warehouse owners who are unwilling to invest in research and development, higher-skilled personnel, and transformation initiatives may be forced to close their doors. This is because automation and robotics, as well as autonomous technologies, will play a vital role in enabling high-speed operations requiring integrated warehouse software solutions and real-time data processing.
Inventory management will be improved with the help of digitization and real-time connection, resulting in lower operating costs.
This will also enable better cooperative load and path planning, and optimize transportation and warehousing infrastructures. As a result, we will see a shift in warehouse/distribution centre methods and an increase in the number of standardized Logistics facilities on the market.
What are the advantages of implementing Digital Warehousing to your Business?
When business decision-makers examine how to improve internal processes, it’s important that they have a full understanding of the intended areas for development. Warehouse staff, business intelligence, and the functional departments can all benefit from a variety of advantages and views. By looking at the big picture, decision-makers can develop a clear plan of action that will help improve internal processes and increase efficiency.
Paperless Digital Warehousing Process
Getting rid of paper in warehouse processes affects not only internal material purchases but also the budget spent on maintenance and management, which is proportional to the amount of paper used in your warehouse. When paper is replaced by mobile scanning equipment, however, the largest and most significant gains are seen in the daily chores performed by personnel.
Fewer (expensive) Mistakes in Digital Warehousing
Common problems in paper-based warehouses include workers taking notes, verifying orders, and putting stuff away while writing on paper with varying degrees of legibility. This can often lead to wasted time and resources spent on deciphering what was written.
Return on Investment in the Short Term for Digital Warehousing
Transparency and the capacity to achieve a clear and concrete ROI within a well-defined timescale are enhanced by easy-to-understand implementation processes and set expenses.
Employees with less training are more efficient in Digital Warehousing
In order to implement a digital warehouse system, new staff must be given the proper training and education. By ensuring that your team is properly informed about the system, you can avoid potential issues and maximize its efficiency.
Processes that are more efficient in Digital Warehousing
Data quality is one of the most important aspects of any business. Without accurate data, it’s impossible to make informed decisions that could help improve or grow the company. This is why it’s so important to have a system in place that can collect and store high-quality data. Additionally, having the ability to access and use this data is just as critical. By making data quality a priority, businesses can set themselves up for success.
Conclusion
Companies should focus on functions that can deliver better value to the business and customers, especially now. A highly optimized digital supply chain has been proven to increase financial performance, including sales and earnings, as well as reducing costs and enhancing the customer journey. Rather than adding new technology onto old systems, companies should take a bold step forward by rethinking their entire supply chain and investing in the innovations that make sense for their operations. By doing this now, you’ll be prepared and ready to hit the ground running when growth returns.


